How to Troubleshoot elasticsearch
You might find yourself attempting to view Elasticsearch logs through Kibana and realize that you have not been receiving logs for quite some time. Unfortunately, elasticsaerch might run into issues and will stop working if the following occur:
- High load from queries (turning indexes red)
- Low disk space (running out of space)
How to check if elasticsearch indexes are in a “red” state.
Method 1 – Terminal
Run the following on your Linux terminal
curl elasticsearchserver:9200/_cat/indices?v

you should see “red” under health.
Alternatively If you have a cluster, you can check the cluster health:
curl 'http://elasticsearchserver:9200/_cluster/health'
you should see your Cluster Name, along with a status”:Red”.
Deleting “Red” Index.
If you have a red index, you can manually remove it by doing the following:
Example: Curl –XDELETE http://elasticsearchserver:9200/indexname
curl -XDELETE http://elasticsearchserver:9200/logstash-winlogbeat-2017.08.07
Re-run the index query and ensure there are no other red indexes.
Method2 – Kibana
Login to your Kibana instance http://elasticsearchserver:5601 and navigate to “Dev Tools”
and paste the following:
GET /_cat/indices?v&s=docs.count:desc
Click the the Green play button ![]()
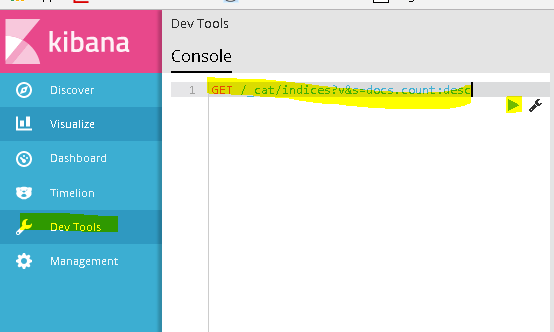
You should see the following:

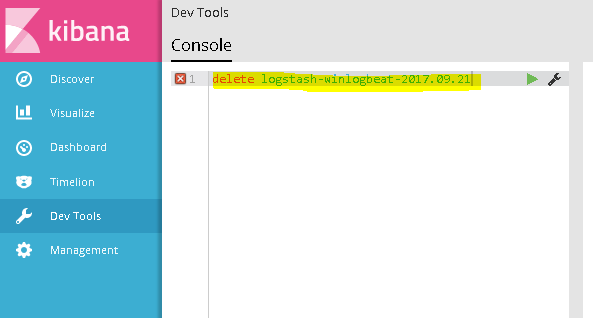
If you do find a red index, you may delete it from here.
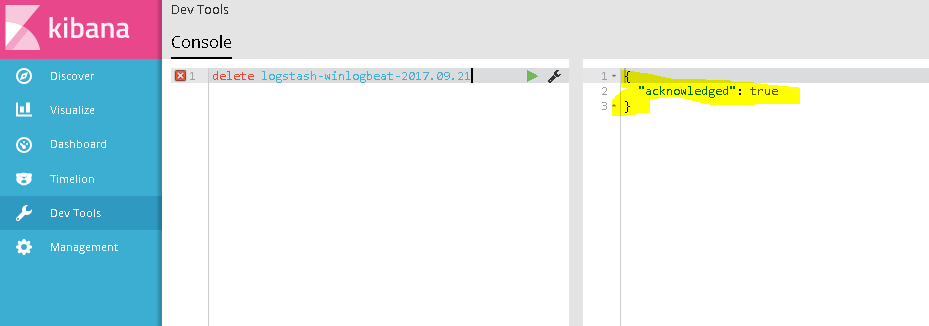
Type the following in the console: delete yourindexname
You should see an “acknowledged: True” message to verify the deletion.
Last Resort: Ran out of disk space
If you ran out of disk space, elasticsearch might just not work at all. You may try to do a curl command, but you might receive a message stating that elasticsearch is not accessible via terminal, or even Kibana.
To verify the disk space in your node run the following command:
df –h
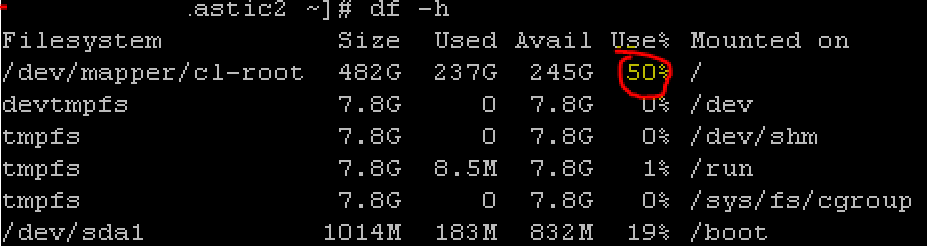
If your elasticsearch node is at 100% capacity, you may have to delete some files manually.
Elasticsearch files will be saved in the following location: /var/lib/elasticsearch/nodes/0/indices
Run the following:
cd /var/lib/elasticsearch/nodes/0/indices
You may run the following to see which folders have the most data
du –h
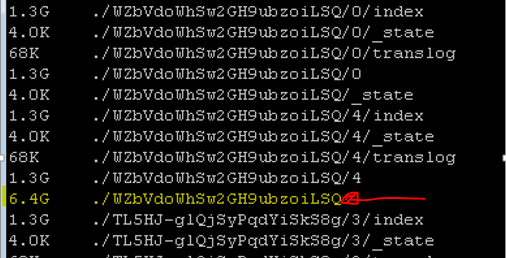
Once you find a folder with x amount of space, you may delete it to clear some space. (Note this might delete unexpected records from a certain time-period, so be careful)
Delete the folder by performing the following:
rm –rf WZbVdoWhSw2GH9ubzoiLSQ/
WzbvdoWhSw2.. is my folder name, change it to yours.
Run df –h to verify that the file was deleted and your disk capacity increased.
Lastly, restart the elasticsearch service:
Service elasticsearch restart
Next Article will go over troubleshooting Logstash.